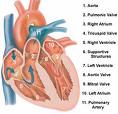
What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common form of heart disease. In CAD the coronary arteries, the vessels that bring oxygen-rich blood to the tissues of the heart, become blocked by deposits of a fatty substance called plaque. As plaque builds, the arteries become narrower and less oxygen and nutrients are transported to the heart. This condition can lead to serious problems, such as angina (pain caused by not enough oxygen-carrying blood reaching the heart) and heart attack. In a heart attack, or myocardial infarction, there is such poor oxygen supply to the heart that part of the heart muscle dies. If a sufficiently large portion of the heart is affected, it may no longer be able to pump blood efficiently to the rest of the body, resulting in death or chronic heart failure.
Approximately 7 million Americans suffer from CAD. It is the leading cause of death among American men and women; more than 500,000 Americans die of CAD-related heart attacks each year.
There are several factors that can each increase the risk of developing CAD:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Diabetes
- Family history of CAD
- Gender
- Age
A person with CAD may or may not have symptoms. Symptoms can include chest pain from angina, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, cold sweats, or nausea.