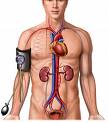
What is EDTA chelation therapy?
Chelation is a chemical process in which a substance is used to bind molecules, such as metals or minerals, and hold them tightly so that they can be removed from a system, such as the body. In medicine, chelation has been scientifically proven to rid the body of excess or toxic metals. For example, a person who has lead poisoning may be given chelation therapy in order to bind and remove excess lead from the body before it can cause damage.
In the case of EDTA chelation therapy, the substance that binds and removes metals and minerals is EDTA (ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid), a synthetic, or man-made, amino acid that is delivered intravenously (through the veins). EDTA was first used in the 1940s for the treatment of heavy metal poisoning. EDTA chelation removes heavy metals and minerals from the blood, such as lead, iron, copper, and calcium, and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in treating lead poisoning and toxicity from other heavy metals. Although it is not approved by the FDA to treat CAD, some physicians and alternative medicine practitioners have recommended EDTA chelation as a way to treat this disorder.